Exploratory Server Installation Instruction
This Note explains how to install Exploratory Server on your machine in your local network.
In the configuration examples in this instruction,
<<version>> means the version of the
Exploratory Server you are installing. Please replace them with the
actual version number string (e.g. 5.5.4.2) when you use them.
Prerequisites
- A server that fulfills system requirements
- Linux OS that fulfills system requirements. **We recommend Ubuntu ** if you have a choice.
- Docker
- Docker Compose
If you don’t have these installed already, take a look at the information below to set them up.
The following OS and Docker version combinations are currently supported.
| Ubuntu version | Docker v20 | Docker v24 |
|---|---|---|
| 16.04 | Supported | - |
| 18.04 | Supported | - |
| 20.04 | Supported | - |
| 22.04 | Supported | Supported |
Also, make sure your user has permission to connect to Docker daemon. - Link
After this, make sure to logout once and log back in.
Ports need to be opened
When using the Exploratory server on-premises, please ensure that the following port numbers are open:
- Port 80 (HTTP)
- Port 443 (HTTPS)
- Port 8080 (HTTP) However, if a different port number is specified during installation, use that number instead.
- Port 3000 (HTTP/WebSocket)
- Port 7000 (Scheduler)
- Port 6311 (Rserve)
- Port 27017 (MongoDB)
Files in the distribution
exploratory-collab-<<version>>.tar.gz- The distribution tarballexploratory-collab-images-<<version>>.tar.gz- Docker images fileexploratory_config.yml- Configuration fileconfigure.sh- Configuration scriptdocker-compose-template.yml- Template for Docker Compose filedefault.conf- Nginx configuration filenginx-webdav.conf- Nginx WebDAV configuration file.data- mongodb data will be stored in this directory.users- User’s shared viz/data will be stored in this directory.ssl- Directory to put SSL certificate files for optional SSL (HTTPS) configuration.
Installation Steps
1. Extract files/directories
Run the following command to extract the files. This also creates exploratory directory.
$ tar xvfz exploratory-collab-<<version>>.tar.gz2. Load Docker image
Run the following command to load the Docker image.
$ cd exploratory
$ docker load -i exploratory-collab-images-<<version>>.tar.gz3. Edit exploratory_config.yml
Open exploratory_config.yml file, which is under the ‘exploratory’ directory created by expanding the compressed distribution file, with editor to modify the configurations.
exploratory_config.yml before modification:
admin_email: you@yourcompany.com
server_port: 8080
license_key: 30daystrial- admin_email - The email address you use as the administrator of the Exploratory Server. Replace the initial value “you@yourcompany.com” with your email address.
- server_port - The port number the Exploratory Server will use. Replace the default port number 8080, if you want to use other port number.
- license_key - Replace “30daystrial” with the license key you have
obtained from Exploratory. If you don’t have a license key yet, please
contact
support@exploratory.io.
**Note:**exploratory_config.yml is a temporary configuration file that is used only at the installation time for easier installation steps. Once the installation is done, modification to exploratory_config.yml is ignored. To make configuration changes after installation, docker-compose.yml, which is a file generated in the following steps, will be the file to be updated.
4. Run configure.sh
Run configure.sh executable file, which is under the ‘exploratory’ directory created by expanding the compressed distribution file. Run the following command.
$ ./configure.sh5. Start Exploratory Server
Run the following command to start Exploratory Server.
$ docker-compose up -dIf you have a problem at starting up the Exploratory Server, please check the “Errors While Starting Up Exploratory Server” section in the How to Fix Common Exploratory Server Problems note.
Once the Exploratory Server is up, open the Exploratory Server on your browser. The format of the URL is like the following. The port number is 8080 by default.
<host name>:<port number>The top page should appear like the following screenshot.
6. Sign in as Admin User
Click “Sign in” link at the right hand side top corner.
Sign in with the admin email address you setup in exploratory_config.yml. The password is ‘welcome1’ by default.
Once signed in, click “Admin” link. You will see admin screen that looks like the following screenshot.
7. Create New Users
7.1. Add User
Click “Users” link.
Click “Create New User” button.
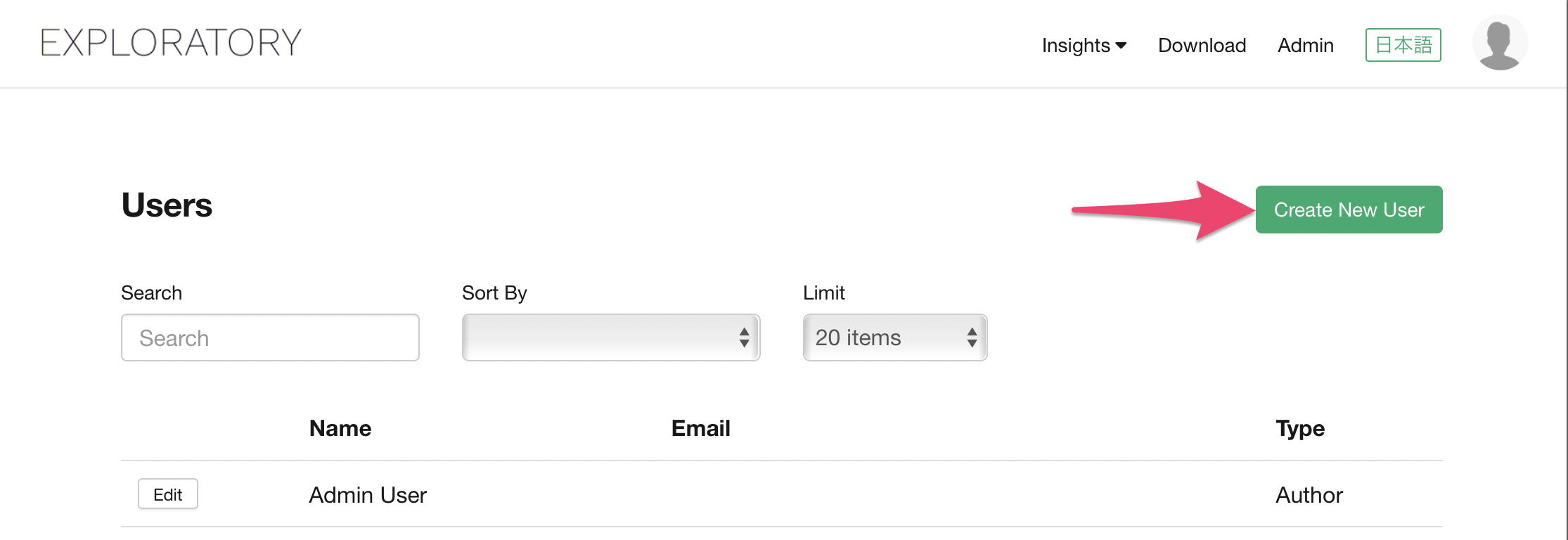
Enter following info about the new user to create, and click “Create” button.
- First name
- Last name
- Email address
- User Type - Select from the following 2 options.
- Author - A user that can use Exploratory Desktop for analysis and reporting.
- Viewer - A user that can view the reports the Author users created and shared. Viewer user cannot use Exploratory Desktop.
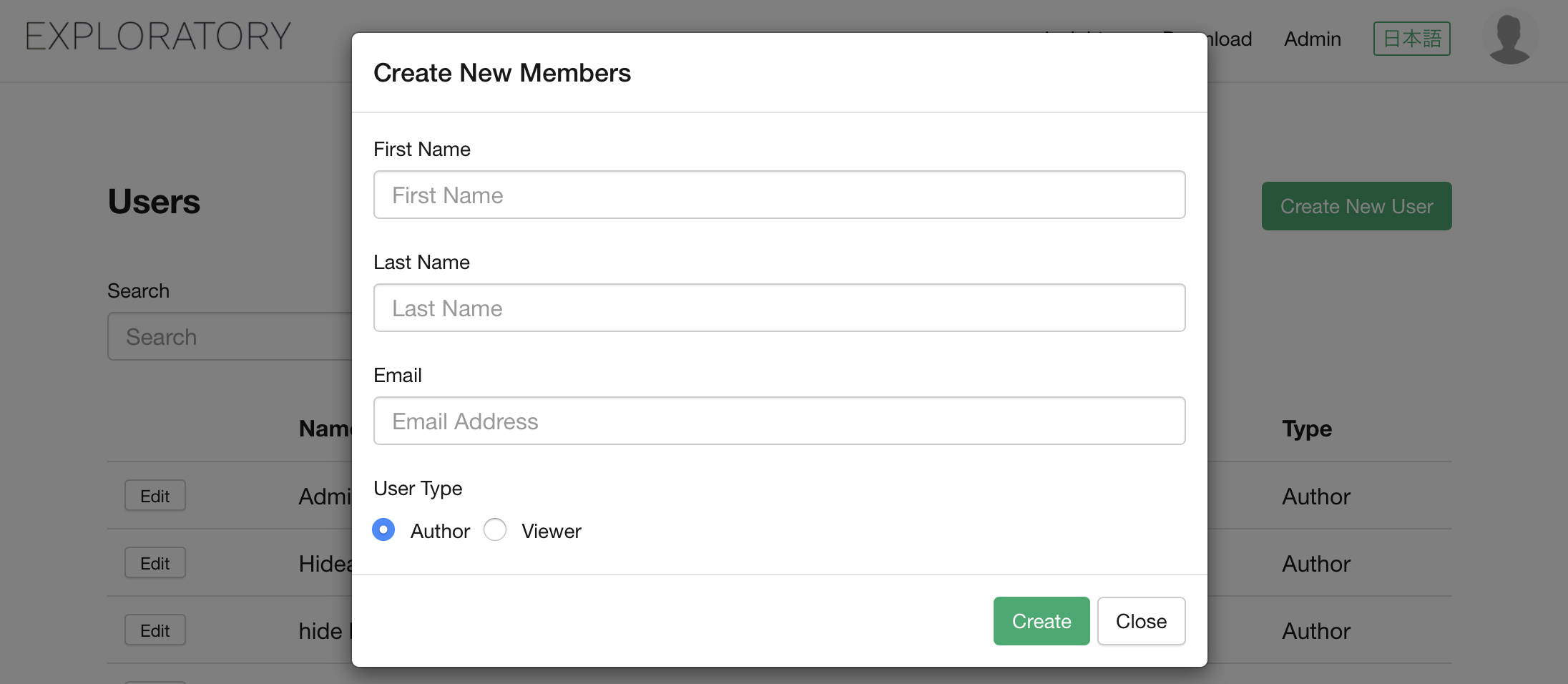
“Create New Member” dialog will show up.
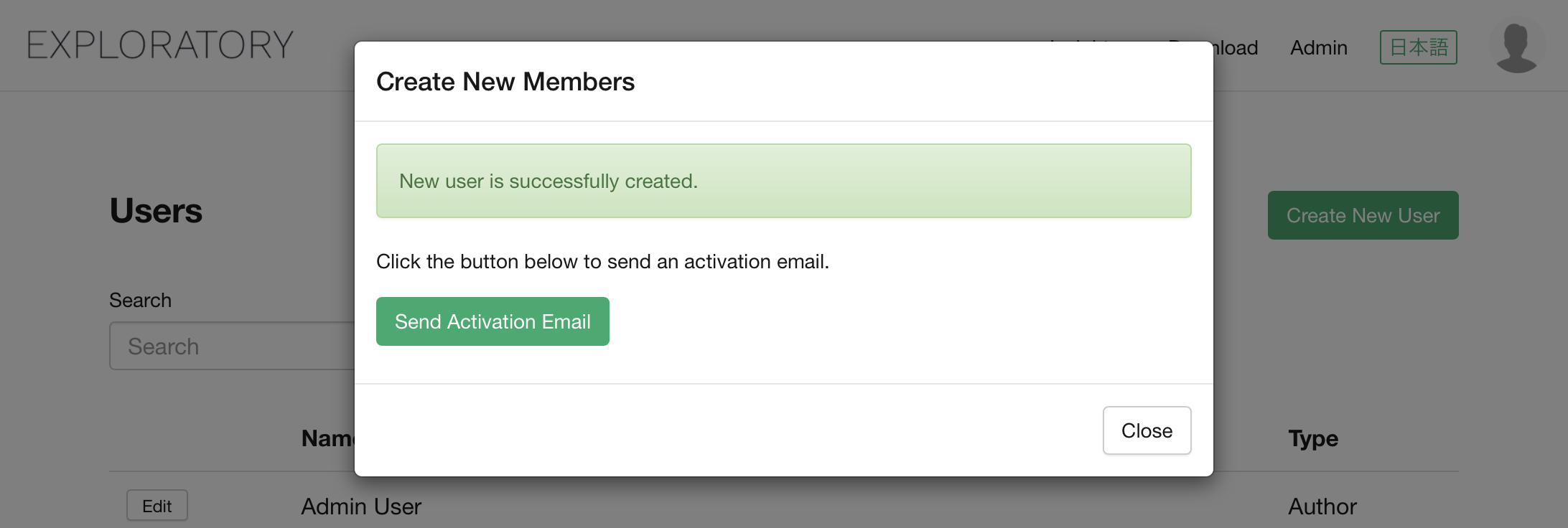
If you click the “Send Activation Email” button, the activation URL will be copied into your email client so that you can just send it to the user, and he/she can click on it to activate.
7.2. Activate User
The new user who receives the activation URL can click the URL to activate the account.
In the pop-up UI, the new user needs to enter:
- First Name
- Last Name
- Password
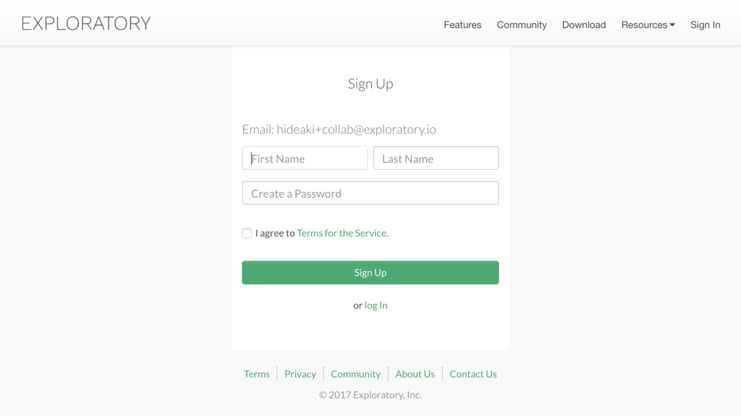
Once it’s activated, then the new user will be redirected to the download page and can start download Exploratory Desktop, if he / she hasn’t done so yet. (If the user already has the latest Exploratory Desktop, he/she can move on to the next step without downloading/installing Exploratory Desktop again.)
Once he or she downloads Exploratory Desktop, then he/she can go to the next step to connect to your Exploratory Server.
Connect to your Exploratory Server
Existing Users
If you have already installed and setup Exploratory Desktop before, you can simply switch the server to your Exploratory Server.
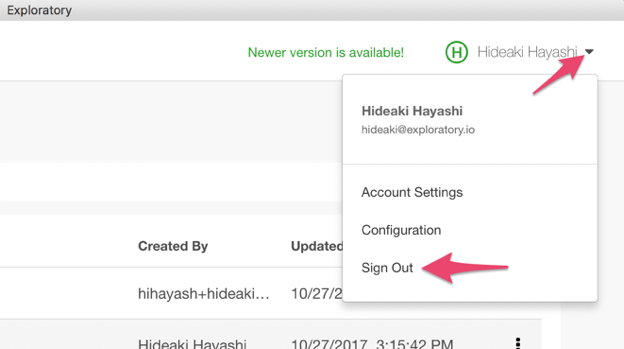
On Exploratory Desktop, in the main page (Project list page), click the triangle icon at the right-hand side top, and click Sign Out menu.
Select ‘Exploratory Server’ for Server Type and type in the URL for your Exploratory Server. Currently, http is the only protocol supported.
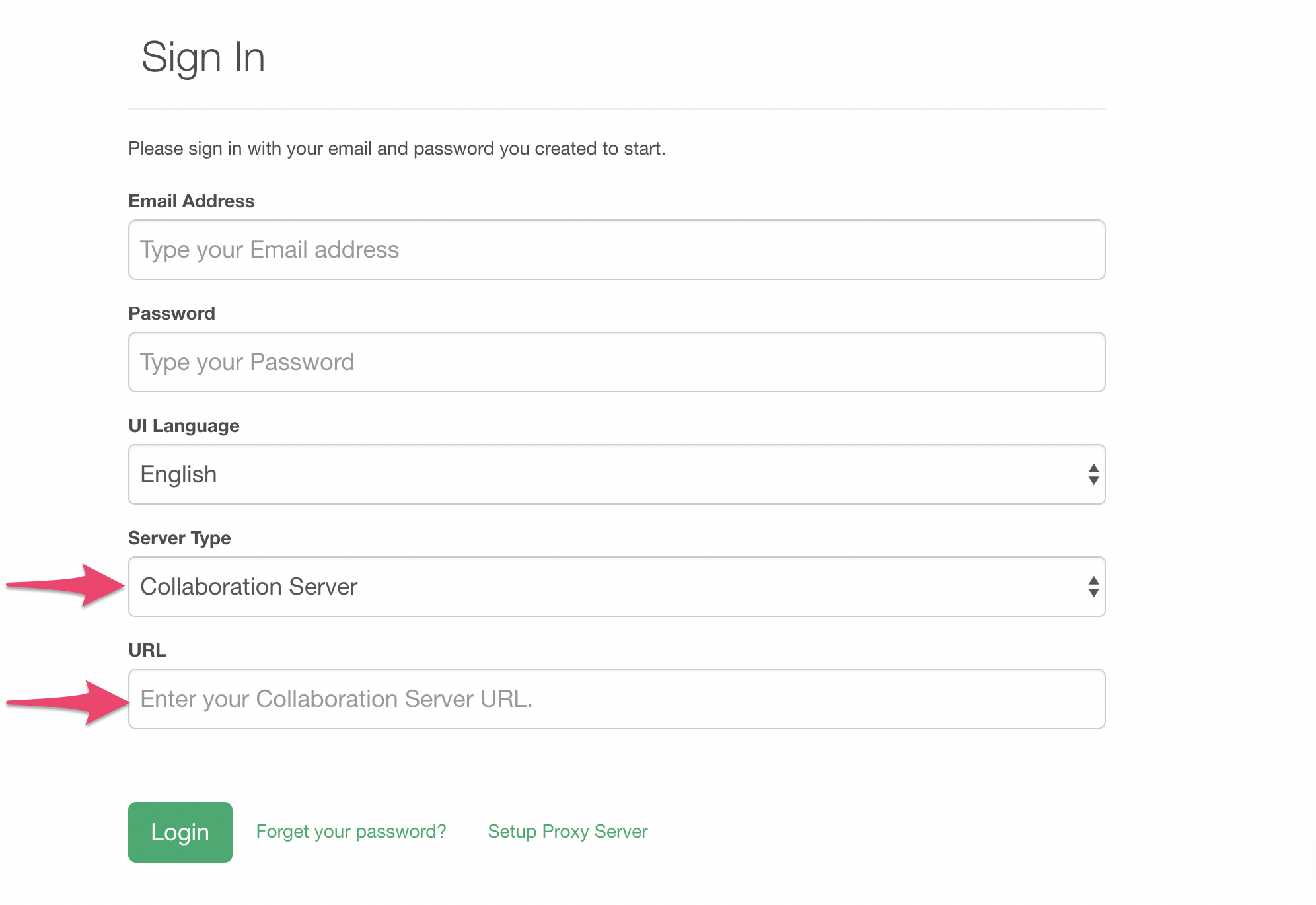
Type in the email address, password, and click “Login” button.
New Users
In the initial Sign In window, type in the URL for your Exploratory Server.
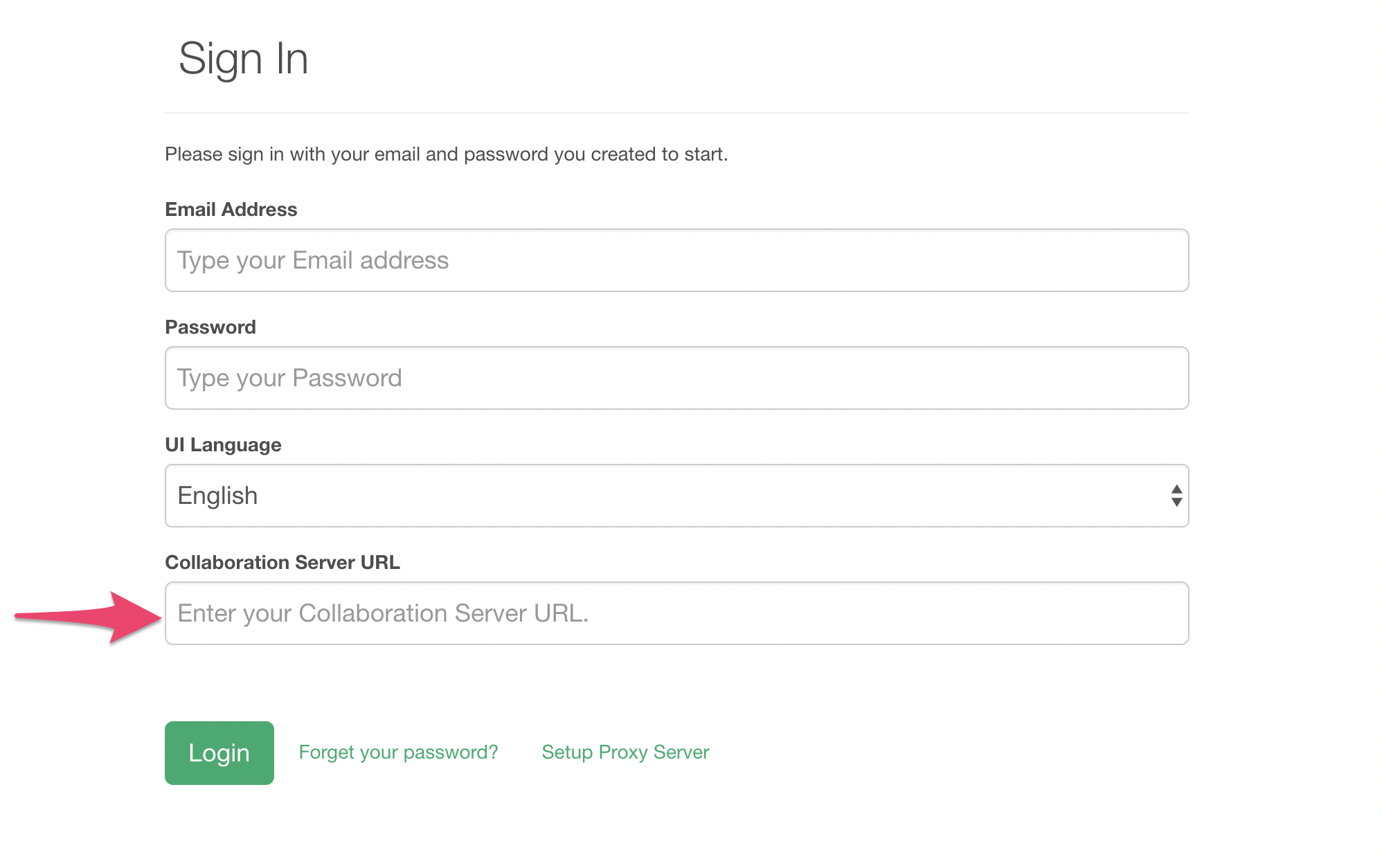
After this, the initial installation process starts and Exploratory Desktop will get ready to start.
Configuration for SSL(HTTPS)
To set up SSL (HTTPS), please follow the instructions in this Note.
Configuration for SMTP Server to Send Notification Emails
You can configure Exploratory Server to send an email notification when an insight is shared, to the users who are invited to see the insight. To do this, add the configurations about the connection to the email server (SMTP server), as explained in this Note.
Backup & Restore
Backup
It is recommended to take a backup regularly for all the files under
the exploratory folder.
How to Restore Exploratory Server from the Backup
Here is how to restore the Exploratory Server from the backup.
- Setup a new machine.
- Restore the
exploratoryfolder from the backup. - Load the Docker images as explained at the Step 2 in the Installation Steps above.
- If the new machine has a different IP address from the original machine and use the domain name to access the Exploratory Server, update the DNS server setting to point the new IP address.
- Start the Exploratory Server and check the connection from the browser.
How to Prevent Google from Indexing Your Exploratory Server
To prevent Google from indexing your Exploratory Server when you set it up on a host accessible from external internet, please take a look at this Note.
How to limit the Admin page access by the IP addresses.
You can set up the IP restriction for Admin pages to limit access to the Admin pages only from the specified IP addresses. Please see this note for the details.
Data Source Setting
Google Drive, Google Cloud Storage, Google Sheets, Google Analytics, and Google BigQuery
Currently, the following OAuth data sources for services from Google are supported.
- Google Drive
- Google Cloud Storage
- Google Sheets
- Google Analytics
- Google BigQuery
If you’d like to use them take a look at the instruction in this Note.
Salesforce
For confiburation to connect to Salesforce using OAuth, take a look at this instruction in this Note.
Types of Available Data Sources
For the types of Data Sources that are currently supported, please take a look at this Note.
Memory Management and Setting
How to Change Memory Allocation
By allocating the appropriate amount of memory, you can improve the performance of the Exploratory Server. For more details, please refer to this guide.
Checking Server Statistics
By executing the following command, you can display the current memory usage, CPU usage, and other statistics of the Docker containers running on the server.
docker statsIf you want to continuously collect statistics, add the
--no-stream option to make the output frequency once per
execution, and run it periodically with a cron command, saving the
output.
docker stats --no-streamTroubleshooting Guide
Common problems and solutions for them can be found in this Troubleshooting Note.